4. Effectiveness evaluation and quantitative analysis system
4.1 Cost benefit analysis model
Establishing a scientific cost-benefit analysis model is the foundation for evaluating the effectiveness of applying Coase's Law. Based on the characteristics of the plastic industry, we have constructed a multidimensional analysis framework.
Direct cost savings analysis
The direct cost changes before and after applying Coase's Law in a certain plastic factory are shown in the following table:
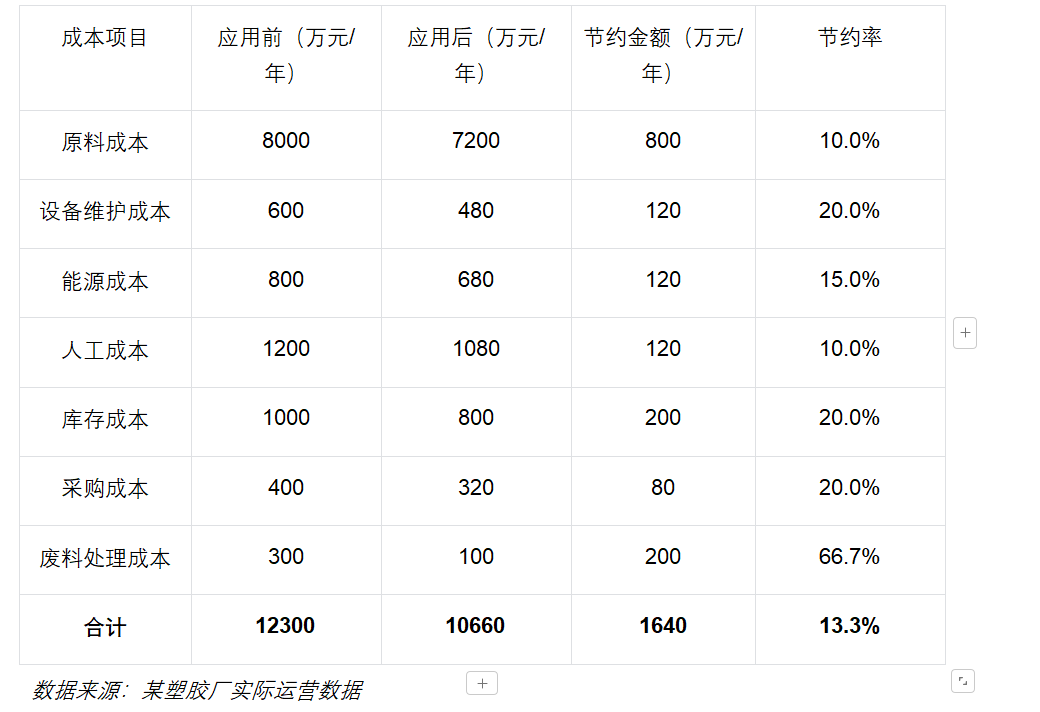
Quantitative analysis of indirect benefits
Although indirect benefits are difficult to quantify directly, they are crucial for the long-term development of enterprises. According to research data, the quantitative estimation of indirect benefits is as follows:
46. Production efficiency improvement: The overall equipment efficiency (OEE) has increased from 65% to 82%, equivalent to a 26% increase in production capacity. Calculated based on an annual production capacity of 100000 tons and a unit price of 10000 yuan/ton, it is equivalent to an increase in output value of 26 million yuan.
47. Product quality improvement: The product qualification rate has increased from 92% to 97%, reducing waste losses by approximately 3 million yuan per year. The customer complaint rate has decreased by 60%, saving approximately 1 million yuan per year in after-sales service costs.
48. Market response speed: The new product development cycle has been shortened from 6 months to 3 months, enabling companies to seize market opportunities faster. It is estimated that the rapid response capability has brought about an additional annual revenue of approximately 5 million yuan to the enterprise.
49. Employee motivation improvement: Through incentive mechanism reform, the per capita output of employees has increased by 30%, while the personnel turnover rate has been reduced from 20% to 8%, saving approximately 2 million yuan/year in recruitment and training costs.
Return on Investment (ROI) Analysis
The investment applied by Coase's Law mainly includes institutional design costs, system construction costs, personnel training costs, etc. The investment and return analysis of a certain plastic factory is as follows:
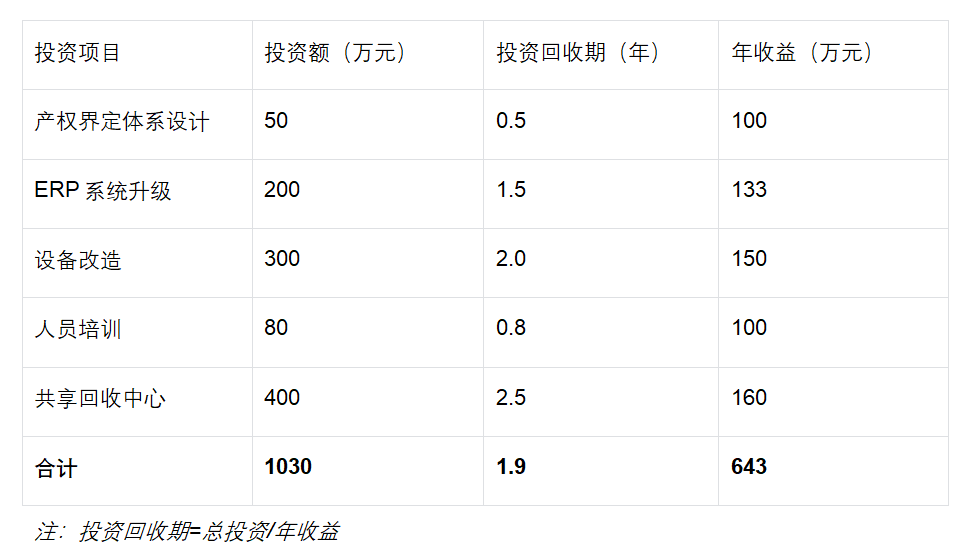
4.2 Key Performance Indicator System
Establishing a scientific KPI system is the key to continuous monitoring and improvement. Based on the characteristics of the plastic industry and the key applications of Coase's Law, we have designed the following indicator system:
Production efficiency index
50. Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE): This is the core indicator for measuring equipment utilization efficiency, calculated using the formula:
OEE=time utilization rate x performance utilization rate x yield rate
The industry's excellent level is over 85%, and a certain plastic factory has increased its OEE from 65% to 82% through the application of Coase's law.
Time utilization rate=(actual running time/planned running time) × 100%
Performance utilization rate=(theoretical output/actual output) × 100%
◦ Yield rate=(number of qualified products/total output) × 100%
51. Capacity utilization rate: reflects the degree of capacity utilization
Capacity utilization rate=(actual output/design capacity) × 100%
The average capacity utilization rate of China's plastic industry in 2024 is 72.3%, and excellent enterprises can reach over 90%.
52. Production cycle: reflects production efficiency
Production cycle=total time from raw material input to finished product output
A certain plastic factory has shortened the average production cycle from 48 hours to 36 hours by optimizing the production process.
Cost control indicators
53. Unit product cost:
Unit product cost=Total cost/Total output
This is the most direct cost control indicator. After applying Coase's law, the unit product cost of a certain plastic factory decreased by 13.3%.
54. Raw material utilization rate:
Raw material utilization rate=(net weight of product/amount of raw material input) × 100%
A certain plastic factory has increased the utilization rate of raw materials from 85% to 92% through waste recycling.
55. Energy consumption rate:
Energy consumption rate=total energy consumption/total output
A certain plastic factory has reduced unit product energy consumption by 15% through equipment renovation and process optimization.
Quality control indicators
56. Product qualification rate:
Product qualification rate=(number of qualified products/total output) × 100%
This is the core indicator of quality management, with a target value usually above 95%.
57. Customer complaint rate:
Customer complaint rate=number of complaint orders/total order quantity x 100%
A certain plastic factory has reduced the customer complaint rate from 5% to 2% by improving its quality control level.
58. Quality cost rate:
Quality cost rate=(prevention cost+appraisal cost+internal loss cost+external loss cost)/total cost x 100%
The target value should be controlled within 5%.
Supply chain efficiency indicators
59. Supplier on-time delivery rate:
On-time delivery rate=number of orders delivered on time/total number of orders x 100%
Through a long-term cooperation agreement, the on-time delivery rate of a plastic factory's supplier has increased from 85% to 95%.
60. Inventory turnover rate:
Inventory turnover rate=cost of sales/average inventory
A certain plastic factory has increased its inventory turnover rate from 6 times per year to 10 times per year through VMI mode and JIT production.
61. Procurement cost reduction rate:
Purchase cost reduction rate=(previous purchase cost - current purchase cost)/previous purchase cost x 100%
A certain plastic factory achieved an annual procurement cost reduction rate of 12% through centralized procurement and long-term agreements.
4.3 Evaluation of Competitiveness Enhancement
The ultimate goal of applying Coase's Law is to enhance competitiveness, which requires comprehensive evaluation from multiple dimensions.
Market position improvement evaluation
According to research data, the market performance comparison of a certain plastic factory before and after applying Coase's Law is as follows:
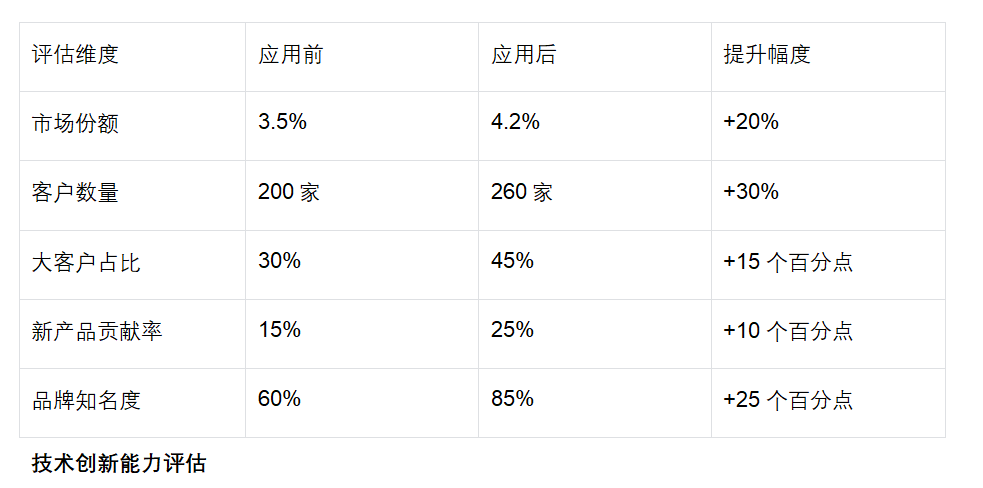
技术创新能力评估
技术创新是企业长期竞争力的源泉。某塑胶厂通过科斯定律应用,技术创新能力显著提升:
62.研发投入占比:从3%提升至5%,达到行业领先水平。
63.新产品开发周期:从6个月缩短至3个月,使企业能够更快响应市场需求。
64.专利申请数量:年均专利申请从5项增加到15项,其中发明专利占比从20%提升至40%。
65.技术人员占比:从15%提升至25%,并建立了完善的技术人员激励机制。
66.产学研合作:与3所高校建立了长期合作关系,共同开展技术研发。
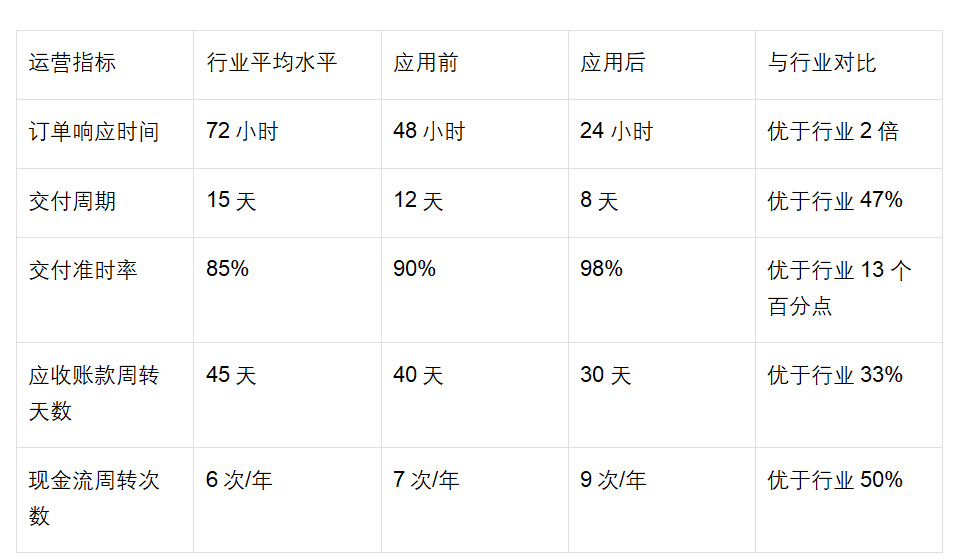
运营效率对比分析
运营效率的提升直接体现了科斯定律应用的效果:
Comprehensive competitiveness score
To comprehensively evaluate the degree of competitiveness improvement, we have established a comprehensive scoring system (out of 100 points):
67. Cost competitiveness (25 points): Based on indicators such as unit product cost and raw material utilization rate, a certain plastic factory scored 22 points (top 15 points for improvement).
68. Quality competitiveness (25 points): Based on indicators such as product qualification rate and customer satisfaction, the score is 23 points (18 points before improvement).
69. Delivery competitiveness (20 points): Based on indicators such as on-time delivery rate and delivery cycle, the score is 19 points (top 13 points for improvement).
70. Technological competitiveness (20 points): Based on indicators such as R&D investment and number of patents, the score is 17 points (11 points before improvement).
71. Innovation competitiveness (10 points): Based on indicators such as new product development capability and market response speed, score 8 points (top 5 points for improvement).
Comprehensive score: 89 points (62 points before improvement), with an improvement rate of 43.5%
5. Risk prevention and response strategies
5.1 Property Rights Definition Risks and Prevention Measures
The definition of property rights is the foundation of the application of Coase's Law, but it faces many risks in the implementation process.
Risk and Response to Property Disputes
Typical problems and solutions encountered by a plastic factory in the process of equipment property rights division:
72. Problem description: There is a dispute between Production Department 1 and Production Department 2 over the right to use a large injection molding machine, and both parties believe that the equipment is crucial for their own production.
73. Risk analysis: Unclear definition of property rights may lead to intensified conflicts between departments, affect production efficiency, and even trigger legal disputes.
74. Response measures:
Establish a Property Rights Definition Committee, composed of representatives from various departments and senior management, responsible for adjudicating property rights disputes
Develop detailed property rights definition rules and clarify the allocation principles of equipment usage rights (such as according to production capacity ratio, frequency of use, etc.)
Establish a property rights change mechanism that allows for the redistribution of usage rights during production plan adjustments, but requires approval from the committee
Establish a transition period, allowing the original user department to continue using it for 3 months before the property rights are officially defined, in order to facilitate a smooth transition
75. Implementation effect: Through the above measures, disputes over equipment usage rights have been successfully resolved, interdepartmental relationships have been improved, and equipment utilization has increased by 15%.
Legal compliance risks and prevention
In the process of defining property rights, it is necessary to ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations:
76. Intellectual property risk: A certain plastic factory did not have a clear agreement on the ownership of intellectual property rights for research and development results in its technical cooperation with suppliers, resulting in disputes in the future.
Preventive measures: Sign a detailed technical cooperation agreement, clarify the ownership of intellectual property rights, and agree on the rights and obligations of both parties
77. Risk of labor regulations: When implementing the internal contracting system, it may involve changes in labor relations.
Preventive measures: Consult with labor law professionals to ensure that the reform plan complies with labor law regulations and protects the legitimate rights and interests of employees
78. Environmental regulation risk: The transfer of waste disposal rights must comply with environmental requirements.
Preventive measures: Select qualified recycling enterprises, sign compliance agreements, and conduct regular environmental audits
79. Antitrust risk: When establishing a shared recycling center, there may be issues of competition within the industry.
Preventive measures: Consult with antitrust legal professionals to ensure that the cooperation agreement does not violate antitrust laws
5.2 Long term agreement performance risk management
Long term agreements are an important means of reducing transaction costs, but there are also performance risks.
Price fluctuation risk and response mechanism
Price risks and countermeasures faced by a long-term procurement agreement signed between a certain plastic factory and its suppliers:
80. Risk scenario: A significant increase in international oil prices leads to a sharp rise in raw material costs, but the mechanism for adjusting agreed upon prices is not flexible.
81. Risk analysis: Price fluctuations may lead to losses for suppliers, affect their willingness to fulfill contracts, or cause the company to lose control of costs.
82. Response mechanism design:
Establish a price adjustment formula: raw material price=base price x (1+fluctuation range of crude oil price x adjustment coefficient)
Set price adjustment trigger condition: When the fluctuation of crude oil price exceeds ± 10%, start the price adjustment program
Upper limit of adjustment range: The price adjustment range shall not exceed ± 5% per time, and the number of adjustments shall not exceed 2 times per year
Establish a risk sharing mechanism: When price fluctuations exceed 20%, both parties shall bear 50% of the excess
83. Implementation case: In March 2025, crude oil prices rose by 25%, triggering a price adjustment mechanism. According to the agreement, the price of raw materials increased by 10%, with the enterprise bearing 5% and the supplier bearing 5%, successfully resolving the price risk.
Supplier default risk and prevention
Supplier management risk prevention and control system of a certain plastic factory:
84. Risk identification:
Supply interruption risk: supplier production equipment failure, raw material shortage, etc
Quality default risk: The quality of the supplied raw materials does not meet the requirements
Delivery delay risk: Failure to deliver goods on time as agreed
85. Preventive measures:
Establish a supplier evaluation system: Regularly evaluate the financial status, production capacity, quality system, etc. of suppliers
Implement supplier grading management: Strategic suppliers, important suppliers, and general suppliers adopt different management strategies
Sign a detailed supply agreement: clarify quality standards, delivery time, breach of contract responsibilities, etc
Establish a supplier backup mechanism: Each key raw material should have at least 2-3 qualified suppliers
86. Emergency plan:
Establish raw material reserves: maintain a safety stock of 15-30 days
Develop an emergency procurement plan: Sign a framework agreement with backup suppliers to ensure supply in emergency situations
Establish a rapid response mechanism: In case of supply issues, activate emergency plans within 24 hours
5.3 Outsourcing Quality Control Risk Prevention
Outsourcing is an important form of applying Coase's Law, but quality control is a key risk point.
Design of Outsourcing Quality Control System
The outsourcing quality control system of a certain plastic factory:
87. Supplier selection control:
Qualification review: Must have relevant production licenses, quality certifications, etc.
On site audit: Conduct on-site inspections of the supplier's production environment, equipment condition, and quality management system
Sample testing: The supplier is required to provide samples for comprehensive quality testing
Small batch trial production: Conduct small batch trial production before formal cooperation to verify quality stability
88. Process monitoring mechanism:
Deploy quality supervisors: Deploy quality personnel to important suppliers for on-site supervision
Establish a quality information system: Real time monitoring of the production process and timely detection of quality issues
Regular quality audit: Conduct a comprehensive quality audit of suppliers once every quarter
Establish a quality warning mechanism: When there are abnormalities in quality indicators, immediately intervene and investigate
89. Inspection and acceptance criteria:
Develop detailed inspection standards, including various indicators such as appearance, size, performance, and environmental protection
Implement full inspection or random inspection: Determine the inspection method based on product characteristics and risk level
Establish a process for handling non-conforming products: clarify the handling methods for returns, exchanges, compensation, etc
◦ Keep quality traceability records: Ensure that product quality issues can be traced back to specific batches and responsible persons
90. Quality improvement mechanism:
Establish a quality problem analysis meeting: hold regular meetings to analyze the causes of quality problems
Implement corrective and preventive measures: Develop improvement measures for quality issues and track and verify them
◦ Conduct quality training: Provide quality awareness and skills training to supplier employees
Establish a quality incentive mechanism: reward suppliers with excellent quality performance
Case analysis of outsourcing risks
Outsourcing quality accident and handling of a certain plastic factory:
91. Accident description: A batch of outsourced products experienced cracking issues during customer use, and the customer requested a return and compensation for the losses.
92. Cause analysis:
The supplier used poor quality raw materials to reduce costs
Inadequate process monitoring and failure to promptly identify quality issues
The inspection standards are not strict, and potential defects were not detected
93. Handling measures:
Immediately activate the emergency plan and recall all relevant batches of products
Apologize to the customer and compensate for the losses, totaling 1.5 million yuan
Negotiate with the supplier, and the supplier will bear 80% of the loss, totaling 1.2 million yuan
Suspend cooperation with the supplier and conduct a comprehensive investigation and rectification
◦ Improve the quality control system, strengthen process monitoring and inspection standards
94. Improvement effect: Through improvement measures, the quality qualification rate of outsourced products has increased from 95% to 99%, and the customer complaint rate has decreased by 80%.
5.4 Adaptive Adjustment to Changes in Market Environment
The changes in the market environment require enterprises to have flexible response capabilities.
Strategies for Dealing with Fluctuations in Raw Material Prices
The price of plastic raw materials will fluctuate significantly in 2025, and a certain plastic factory's response measures:
95. Price monitoring system:
Establish a raw material price monitoring system to track international oil prices, plastic futures prices, etc. in real time
Prepare daily price analysis reports and predict price trends
Establish a price warning mechanism to issue alerts when price fluctuations exceed 5%
96. Inventory strategy adjustment:
When the price is at a low level, increase strategic inventory appropriately, with a maximum usage of no more than 2 months
When the price is at a high level, reduce inventory and adopt small batch and multi frequency procurement
Using futures instruments for hedging and locking in some raw material costs
97. Cost transfer mechanism:
Negotiate with customers and establish a price linkage mechanism
When the fluctuation of raw material prices exceeds 10%, the product price can be adjusted
Develop high value-added products and reduce sensitivity to raw material prices
98. Supply chain optimization:
Search for alternative raw materials to reduce dependence on a single raw material
Strengthen strategic cooperation with suppliers to jointly cope with price fluctuations
◦ Improve raw material utilization efficiency and reduce raw material consumption per unit product
Response to changes in environmental policies
Faced with increasingly strict environmental requirements, a plastic factory's adaptability adjustment:
99. Policy tracking mechanism:
Assign a dedicated person to be responsible for tracking environmental policies and keeping abreast of policy trends in a timely manner
Maintain communication with the environmental protection department and obtain the latest policy interpretation
◦ Participate in industry association activities to understand industry environmental requirements
100. Technological upgrade path:
Develop an environmental protection technology renovation plan and gradually phase out high polluting processes
Invest in clean production technologies such as solvent-free coating, water-based coatings, etc
Develop new biodegradable and recyclable products
101. Circular Economy Layout:
◦ Increase investment in waste recycling and improve resource recycling efficiency
Establish a product recycling system to achieve closed-loop production
Collaborate with upstream and downstream enterprises to build a circular economy industry chain
102. Compliance Management System:
Establish a sound environmental management system and operating procedures
Regularly conduct environmental training to enhance employees' awareness of environmental protection
◦ Entrust third-party organizations to conduct environmental monitoring and evaluation
Responding to changes in the international trade environment
Faced with a complex international trade environment, a plastic factory's response strategy:
103. Market diversification:
Reduce dependence on a single market and explore emerging markets
Strengthen the development of the domestic market and increase the proportion of domestic sales
◦ Develop business in countries along the "the Belt and Road"
104. Product structure adjustment:
Develop products that meet the standards of the importing country
◦ Improve product technology content and obtain technical barrier protection
Develop independent brands and increase product added value
105. Localization of supply chain:
Establish production bases or partners in major export markets
Adopting localized procurement to reduce trade risks
◦ Utilize free trade agreements to enjoy tariff preferences
106. Risk hedging tools:
Using financial instruments such as forward foreign exchange settlement and sale to hedge exchange rate risk
◦ Purchase export credit insurance to reduce foreign exchange risk
Establish risk reserves to cope with sudden trade frictions
6. Differentiated application strategies for different types of plastic factories
6.1 Strategy selection classified by enterprise size
6.1.1 Small plastic factory (annual revenue<50 million)
Due to limited resources, small plastic factories should adopt a "small but refined" application strategy.
The application practice of Coase's Law in a small plastic factory (with an annual revenue of 30 million yuan):
107. Internal optimization is the main focus:
◦ Key equipment property rights division: Contract 3 injection molding machines to 3 teams respectively, implement "charter to person"
Establish a simple incentive mechanism: If the equipment utilization rate reaches 80% or above, a reward of 500 yuan/month will be given; Save raw material costs, employees can receive 30%
Implementation effect: Equipment utilization rate increased from 65% to 78%, saving an average monthly cost of 30000 yuan
108. Supply chain simplification:
Establish long-term cooperative relationships with 2-3 core suppliers and sign framework agreements
Adopting the "small batch, multi frequency" procurement model to reduce inventory pressure
Reduce costs through joint procurement: Collaborate with two other small factories to achieve an annual procurement volume of 5000 tons and receive a 10% price discount
109. Outsourcing of waste disposal:
Outsourcing the waste disposal rights to professional recyclers, with an annual recycling revenue of approximately 500000 yuan
◦ No need to invest in waste treatment equipment, saving 2 million yuan in investment
Focus on core business, increase annual profit margin by 3 percentage points
110. Investment advice:
Initial investment: 500000 yuan (system design, employee training, etc.)
Expected revenue: Annual cost savings of 800000 to 1 million yuan
◦ Investment payback period: 0.6-0.8 years
6.1.2 Medium sized plastic factory (annual revenue of 50-50 billion)
Medium sized plastic factories should adopt a strategy of "internal and external improvement", actively expanding external cooperation while optimizing internally.
Comprehensive application plan for a medium-sized plastic factory (annual revenue of 200 million yuan):
111. Internal management upgrade:
Establish a business unit system: Divide the enterprise into three business units, with each unit accounting independently
Implement comprehensive budget management: Each business unit independently formulates the budget, and the headquarters coordinates it
Establish an internal market-oriented mechanism: Transactions between business units are conducted at market prices
Effect: Management efficiency increased by 30%, cost reduced by 8%
112. Supply chain integration:
Establish a strategic alliance with upstream raw material suppliers, take a 5% stake, and obtain stable supply and price discounts
Implement VMI model: The main raw materials are managed by suppliers to reduce inventory costs by 30%
Develop 2-3 alternative suppliers to reduce supply risks
Annual savings of 12 million yuan in procurement costs
113. Capacity sharing platform:
Collaborate with 5 peer enterprises to establish a shared recycling center, invest 8 million yuan, and hold a 20% stake
Annual processing of 3000 tons of waste, with a recycling value of 6 million yuan
Reduce waste disposal costs by 40% and save 1.5 million yuan annually
114. Technological innovation cooperation:
Collaborate with universities to establish research and development centers and jointly develop new products
The proportion of R&D investment has increased to 4%, and the contribution rate of new products has reached 25%
Received a government innovation subsidy of 2 million yuan
115. Investment and returns:
Total investment: 20 million yuan
Expected annual revenue: 20-25 million yuan
◦ Investment payback period: 1 year
6.1.3 Large plastic factory (annual revenue>500 million)
Large plastic factories should adopt an "ecological construction" strategy to build an industrial ecosystem.
Strategic layout of a large plastic group (with annual revenue of 2 billion yuan):
116. Group control mode:
Adopting a strategic control model: the group is responsible for strategic planning, capital operations, and brand management
Subsidiaries operate independently: Each subsidiary accounts independently and has significant autonomy
Establishing an internal capital market: Unified allocation of funds within the group to improve the efficiency of fund utilization
Implementation effect: Reduced capital costs by 2 percentage points, saving 40 million yuan in annual financial expenses
117. Industrial chain integration:
◦ Upstream Extension: Acquiring a raw material production enterprise to ensure raw material supply
Expand downstream: Establish a plastic product sales company to control the end market
Horizontal integration: Acquiring 3 peer companies to achieve economies of scale
Industrial chain synergy effect: overall cost reduction of 15%, market share increased to 8%
118. Circular economy system:
Establish a park level shared recycling system, covering 10 surrounding enterprises
Invest in the construction of chemical recycling facilities to convert waste into raw materials
Annual processing of 20000 tons of waste, with a recycling value of 40 million yuan
Received support from government circular economy demonstration projects, with a subsidy of 50 million yuan
119. Digital transformation:
◦ Build an industrial Internet platform to realize the digitalization of the whole industrial chain
Applying artificial intelligence to optimize production planning, reducing inventory by 25%
Establish a big data center to accurately predict market demand
The efficiency improvement brought by digitization creates an annual value of 100 million yuan
120. International layout:
Establishing production bases in Southeast Asia to avoid trade barriers
Acquiring European technology companies to acquire advanced technology
Establish a global supply chain system to achieve optimized resource allocation
Overseas business accounts for 30%
121. Investment and return:
5-year total investment: 1.5 billion yuan
Expected annual revenue: 300-400 million yuan
◦ Boosting enterprise valuation: market value increased from 5 billion to 8 billion
6.2 Strategy selection by product type
6.2.1 Daily Plastic Products Factory
Daily plastic product factories are facing fierce price competition and should focus on improving competitiveness through cost control.
Application of Coase's Law in a Daily Plastic Products Factory:
122. Cost leadership strategy:
Implement lean production: reduce production costs by 15% by eliminating waste
Optimize product design: reduce unnecessary functions and lower material costs
Standardized production: Developing universal molds to reduce mold costs by 30%
123. Supply chain optimization:
Establish long-term cooperation with raw material suppliers and lock in prices
◦ Adopt centralized procurement, with an annual procurement volume of 100000 tons, and receive a 15% price discount
Develop application technology for recycled materials, using 30% recycled materials to reduce costs by 20%
124. Channel integration:
Establish direct supply relationships with large supermarkets to reduce intermediate links
Develop e-commerce channels and reduce channel costs
Establish your own brand and increase product added value
125. Efficient utilization of waste:
Establish an internal waste recycling system with a recycling rate of 95%
Develop waste granulation technology to achieve 100% utilization of waste
Annual savings of 8 million yuan in raw material costs
6.2.2 Industrial Accessories Plastic Products Factory
Industrial accessory plastic product factories have high requirements for quality and accuracy, and should focus on improving their technical capabilities and quality control levels.
The transformation and upgrading path of a certain industrial accessory plastic factory:
126. Driven by technological innovation:
Establish a research and development center, with R&D investment accounting for 6%
Synchronize development with the host factory and participate in product design
Obtained 20 patents, including 5 invention patents
The product accuracy reaches ± 0.05mm, meeting the needs of high-end customers
127. Quality Management System:
Establish IATF16949 automotive industry quality system
Implement full process quality control, with a product qualification rate of 99.5%
Establish a traceability system to achieve full lifecycle management of products
128. Deepening customer relationships:
Establish strategic partnerships with core customers and participate in their new product development
◦ Provide customized solutions to increase customer stickiness
Obtain long-term supply agreements to ensure stable orders
129. Intelligent manufacturing upgrade:
Introducing Industry 4.0 technology and building smart factories
◦ Achieve flexible production and quickly respond to customer needs
Production efficiency increased by 40%, product delivery time shortened by 50%
6.2.3 Medical Plastic Products Factory
Medical plastic product factories face strict regulatory requirements and should focus on compliance and quality control.
Compliance management strategy of a certain medical plastic products factory:
130. Regulatory Compliance Management:
Establish a comprehensive quality management system and obtain ISO13485 certification
Strictly implement the quality management standards for medical device production
Establish a product traceability system to ensure traceability
Regularly conduct internal audits and management reviews
131. Supply chain control:
Raw material suppliers must obtain FDA or CE certification
Establish a supplier audit system and conduct regular on-site audits
Implement strict incoming inspection to ensure the quality of raw materials
132. Construction of technical barriers:
Focus on high-end medical products such as heart stents, artificial joints, etc
Collaborate with medical institutions to jointly develop new products
Obtained multiple medical device registration certificates
Establish a technological moat to avoid low price competition
133. Risk Management System:
Establish a comprehensive risk management process
Conduct a thorough risk assessment of the product
Develop emergency plans to respond to quality accidents
Purchase product liability insurance and transfer risks
6.3 Strategy selection classified by market positioning
6.3.1 OEM Plastic Factory
OEM plastic factories should focus on improving production efficiency and cost control capabilities.
Transformation and upgrading strategy of a certain OEM plastic factory:
134. Lean Production Implementation:
Introduce the concept of lean production and eliminate the seven major wastes
Implement rapid mold change (SMED), reducing mold change time from 2 hours to 15 minutes
Establish a pull based production system to reduce inventory by 60%
Increase per capita output by 50%
135. Flexible manufacturing capability:
◦ Build flexible production lines that can quickly switch products
Develop modular production technology to improve production flexibility
The minimum order quantity has been reduced from 10000 pieces to 1000 pieces
The delivery time has been shortened from 15 days to 3 days
136. Cost advantage enhancement:
Reduce unit costs through economies of scale
◦ Optimize production processes and improve material utilization
Automation transformation to reduce labor costs
Reduce total costs by 15% and maintain price competitiveness
137. Customer service improvement:
Establish a rapid response mechanism and respond to customer needs within 24 hours
Provide one-stop services, including design, sampling, production, and packaging
Establish a customer satisfaction evaluation system and continuously improve it
6.3.2 ODM Design and Manufacturing Plastic Factory
ODM plastic factories should focus on improving their design capabilities and innovation levels.
The innovative development path of a certain ODM plastic factory:
138. Design capacity building:
Establish an industrial design center with 30 designers
Introduction of CAD/CAE/CAM integrated design system
Develop 100 new products annually, with a product update rate of 40%
Design service revenue accounts for 20%
139. Intellectual Property Management:
Establish a comprehensive intellectual property management system
Apply for patent protection for design schemes in a timely manner
Sign a confidentiality agreement with the client to protect the design results
Establish a design library to achieve design resource sharing
140. Investment in technological innovation:
R&D investment accounts for 8%, higher than the industry average
Collaborate with universities to jointly develop new materials and processes
◦ Obtained recognition as a provincial-level enterprise technology center
The profit growth brought by technological innovation has reached 30%
141. Brand value enhancement:
Gradually transitioning from OEM to ODM to increase design added value
Establish independent brands and gain recognition in segmented markets
Design services have gained customer recognition, with an annual increase of 50% in design fee income
6.3.3 Self owned brand plastic factory
Independent brand plastic factories should focus on building brand influence and channel control.
The path of brand building for a certain independent brand plastic enterprise:
142. Brand Strategy Planning:
Clear brand positioning: high-end environmentally friendly plastic products
Establish a brand identity system, including logo, packaging, promotion, etc
Develop brand communication strategies to enhance brand awareness
143. Channel system construction:
Establish a sales channel that integrates online and offline channels
Joined mainstream e-commerce platforms with annual sales exceeding 100 million
◦ Open brand exclusive stores to enhance brand image
Develop a dealer network that covers major cities across the country
144. Product innovation capability:
Establish a user research center to gain a deeper understanding of consumer needs
Every year, 100 new products are launched to maintain their freshness
Develop intelligent products, such as smart storage boxes, smart flower pots, etc
The gross profit margin of the product has reached 45%, far higher than that of the OEM business
145. Supply chain integration:
◦ Control the core production process to ensure stable quality
Establish a supplier management system to ensure the quality of raw materials
Investing in the construction of automated factories to improve production efficiency
Fast supply chain response speed, shortened new product launch cycle to 3 months
7. Analysis and Response to External Environmental Impact
7.1 Impact and Response to Changes in Economic Situation
In 2025, the global economy will face many uncertainties, and the plastic industry, as an important component of the manufacturing industry, will be significantly affected.
Macroeconomic Environment Analysis
According to the latest economic data, the global and Chinese economic situation in 2025 will present the following characteristics:
146. Global economic slowdown: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) predicts a global economic growth rate of 3.1% by 2025, lower than the historical average. The US economy is affected by high interest rates, resulting in sluggish growth; The European economy is facing an energy crisis and inflationary pressures; The growth differentiation of emerging market countries is obvious.
147. China's economy seeks progress while maintaining stability: China's GDP growth target for 2025 is around 5%, and the economic structure continues to be optimized. The manufacturing PMI remains above the boom bust line, but the growth rate has slowed down. The consumer market is gradually recovering, but consumer confidence still needs to be boosted.
148. The trade environment is complex and constantly changing: the trade friction between China and the United States continues, and the United States has imposed a 30% tariff on Chinese plastic products (including 20% fentanyl related fees and a 10% base tariff). The EU implements the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) and imposes carbon taxes on high carbon emitting products.
The specific impact on the plastic industry
149. Demand side impact:
◦ Weak consumer demand: Consumer purchasing power declines, slowing growth in demand for plastic products
◦ Decreased export orders: Trade barriers lead to increased export costs, and orders are transferred to Southeast Asia and other regions.
Structural opportunities: Rapid demand growth in fields such as new energy, healthcare, and environmental protection
150. Supply side impact:
Raw material price fluctuations: Crude oil prices have intensified, with PP prices rising from 8850 yuan/ton to 13000 yuan/ton in March 2025, a 46% increase
◦ Overcapacity pressure: Some traditional plastic products have overcapacity, intensifying competition
◦ Technology upgrade demand: Environmental protection requirements have increased, forcing enterprises to upgrade their technology.
151. Cost impact:
Rising energy costs: Electricity and natural gas prices have risen, increasing production costs
◦ Increased logistics costs: Transportation costs have risen, especially in international logistics
Increased compliance costs: Compliance requirements such as environmental protection and safety increase the burden on enterprises
Enterprise response strategy
Faced with a complex economic environment, plastic companies should take the following measures:
152. Demand side management:
Optimize product structure: reduce low value-added products and increase the proportion of high value-added products
◦ Developing emerging markets: focus on countries along the "the Belt and Road", Africa, Latin America and other markets
Deeply cultivating the domestic market: seizing the opportunity of the domestic circulation and increasing the proportion of domestic sales
Innovative Business Models: Developing New Models such as C2M and Personalized Customization
153. Supply side reform:
◦ Capacity optimization adjustment: eliminate outdated production capacity and transform towards high-end and intelligent production.
Driven by technological innovation: increase R&D investment, develop new materials and processes
Industrial Chain Collaboration: Strengthening Upstream and Downstream Cooperation, Building a Stable Supply Chain
Green and low-carbon transformation: developing circular economy and achieving sustainable development
154. Cost control measures:
◦ Lean Production: Reduce production costs by 10-15% through lean management
Digital Transformation: Utilizing digital technology to improve efficiency and reduce operating costs
Supply chain optimization: Reduce raw material costs through centralized procurement, long-term agreements, etc
Financial instrument application: using futures, options and other tools to hedge price risks
7.2 The impact and response of stricter environmental policies
The increasingly strict environmental policies are profoundly changing the development pattern of the plastic industry.
Analysis of Changes in Policy Environment
The environmental protection policies in 2025 will present the following characteristics:
155. Domestic policy trends:
Deepening the promotion of the "dual carbon" goal: it is required to achieve carbon peak before 2030 and carbon neutrality before 2060
Strengthening the Control of Plastic Pollution: The "Opinions on Further Strengthening the Control of Plastic Pollution" require that by 2025, key areas should basically achieve the reduction, substitution, and standardized recycling of plastic products
◦ Emission standards raised: further tightening of emission standards for air and water pollutants
Circular Economy Development: Encourage the Development of Biobased Materials, Degradable Plastics, and Recycled Plastics
156. International policy requirements:
◦ EU Circular Economy Strategy: Requires PET bottle recycling material content to reach 25% by 2025 and 30% by 2030
Environmental regulations in the United States: California requires a plastic bottle recycling rate of 50% by 2025 and 90% by 2030
Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism: EU CBAM imposes carbon tax on high carbon emission products
Ocean Plastic Pollution Control: The International Community Intensifys Efforts to Control Ocean Plastic Pollution
157. Local policy practice:
◦ Plastic ban upgrade: Some cities will expand the ban to all non degradable plastic bags
Refined plastic restriction measures: stricter requirements are proposed for disposable plastic tableware, takeaway packaging, etc
◦ Recycling System Construction: Establish a sound garbage classification and recycling system
Strengthening environmental law enforcement: increasing frequency of environmental inspections and intensified penalties
The impact on business operations
158. Production and operation impact:
Technical transformation cost: Enterprises need to invest in clean production technology, and the transformation cost accounts for 3-5% of annual revenue
Change in raw material selection: Degradable or high recyclable materials must be used, resulting in a cost increase of 10-20%
Production process adjustment: It is necessary to adjust the production process to meet environmental requirements
Product structure transformation: Some traditional products are facing elimination and new products need to be developed
159. Market access threshold:
◦ Environmental permit requirements are stricter, increasing the difficulty of approval
◦ Need to pass clean production audit, environmental management system certification, etc.
Some regions have implemented total production capacity control, making it difficult to approve new projects
Export products need to meet the environmental standards of the importing country
160. Increased compliance costs:
Operating costs of environmental protection facilities: The operating costs of waste gas treatment, sewage treatment and other facilities account for 5-8% of the total cost
◦ Environmental monitoring costs: Increased costs for regular monitoring, third-party testing, etc.
Environmental management expenses: Professional environmental management personnel are required
High cost of illegal activities: Once violated, there is a risk of huge fines and production suspension
Enterprise response strategy
Faced with increasingly strict environmental policies, plastic companies should proactively adapt and turn challenges into opportunities:
161. Driven by technological innovation:
◦ Clean production technology: adopting solvent-free and low VOC production processes
Recycling technology: Developing chemical recycling technology for waste materials to achieve raw material recycling
Green material research and development: invest in new materials such as bio based plastics and biodegradable plastics
Energy saving and emission reduction technology: reducing energy consumption and emissions through technological transformation
162. Product structure adjustment:
Develop green products: Develop biodegradable and recyclable environmentally friendly products
High Value Added Transformation: Expanding into High Value Added Fields such as Medical Devices and Electronic Appliances
Circular economy products: Design products that are easy to recycle and recyclable
◦ Customized service: Provide environmental solutions according to customer needs
163. Management System Upgrade:
Establish an environmental management system: certified with ISO14001 and other certifications
Implement clean production: conduct regular clean production audits
Environmental compliance management: Establish a sound environmental management system and emergency plan
◦ Information Disclosure and Transparency: Proactively disclose environmental information to enhance corporate image
164. Win win cooperation model:
Industrial chain collaboration: Collaborate with upstream and downstream enterprises to jointly promote green development
Industry university research cooperation: Collaborate with universities and research institutes to jointly develop environmental protection technologies
Industry Joint Action: Participate in industry associations to jointly address environmental challenges
International Cooperation and Exchange: Learning and Drawing on Advanced International Experience and Technology
7.3 Impact and Response to Changes in the International Trade Environment
The complex changes in the international trade environment have had a significant impact on the export business of the plastic industry.
Analysis of Changes in Trade Environment
The international trade environment in 2025 will present the following characteristics:
165. Trade protectionism is on the rise:
◦ Increased tariff barriers: US imposes 30% tariff on Chinese plastic products
Non tariff barriers: Technical standards, environmental requirements, intellectual property rights, etc. have become new trade barriers
Trade transfer effect: Orders are transferred from China to Southeast Asia, India and other countries
166. Restructuring of Regional Trade Agreements:
RCEP implementation: Reduction of trade barriers within the region, bringing opportunities for businesses
European American Trade Agreement: Strengthening trade cooperation between Europe and the United States may pose new challenges to Chinese enterprises
Bilateral trade negotiations: China actively promotes bilateral trade agreements with other countries
167. Adjustment of supply chain pattern:
Localization of Supply Chain: Countries Promote Localization of Key Industrial Chains
Supply Chain Diversification: Enterprises seek supply chain diversification to reduce risks
The rise of nearshore outsourcing: developed countries tend to purchase locally
168. Increased exchange rate fluctuations:
The strengthening of the US dollar: The fluctuation of the RMB exchange rate against the US dollar has increased
◦ Increased exchange rate risk: Enterprises face greater exchange rate risk
Diversification of settlement currencies: Enterprises seek diversification of settlement currencies
The impact on plastic export enterprises
169. Direct impact:
Rising export costs: Tariff increases directly raise export product prices, reducing competitiveness
Order loss: Some customers have turned to other suppliers, resulting in a 20-30% decrease in order volume
Profit decline: Even if maintaining market share, profit margins have significantly decreased
170. Indirect impact:
◦ Decreased capacity utilization: reduced export orders leading to overcapacity
◦ Increased financial pressure: Extended accounts receivable collection cycle, difficult capital turnover
Decreased investment willingness: Enterprises are becoming more cautious in investing due to increased uncertainty about the future
171. Structural impact:
Product structure adjustment: Need to transform towards high value-added products
Market structure adjustment: It is necessary to explore emerging markets and reduce dependence on the European and American markets
Changes in trade modes: the need to develop new models such as cross-border e-commerce and overseas warehouses
Enterprise response strategy
Faced with a complex international trade environment, plastic export enterprises should adopt diversified response strategies:
172. Market diversification:
· Deepen the "the Belt and Road" market: focus on developing markets in ASEAN, the Middle East, Africa, Latin America, etc.
Strengthening RCEP regional cooperation: fully utilizing RCEP preferential policies and expanding intra regional trade
Developing the domestic market: shifting some export capacity to the domestic market
Exploring Emerging Markets: Focus on Market Opportunities in Emerging Economies such as India and Brazil
173. Product upgrade and transformation:
Driven by technological innovation: developing high-end products with independent intellectual property rights
Differentiated competition: providing customized and personalized products and services
Brand building: Developing independent brands and increasing product added value
Green Product Development: Develop products that meet international environmental standards
174. Trade model innovation:
Cross border e-commerce development: Utilizing cross-border e-commerce platforms to directly reach overseas consumers
Overseas warehouse construction: Establish overseas warehouses in major markets to shorten delivery cycles
◦ Transit trade strategy: Avoid trade barriers by transiting through a third country
Expansion of Service Trade: Developing Intangible Trade such as Technology Services and Design Services
175. Risk management measures:
Exchange rate risk hedging: using forward foreign exchange settlement and sale, options and other tools to hedge exchange rate risk
◦ Trade risk prevention: Purchase export credit insurance to reduce foreign exchange risk
Supply chain risk control: Establish a diversified supply chain to reduce the risk of supply interruption
Compliance risk management: Strengthen export compliance management to avoid trade frictions
176. Deepening International Cooperation:
Overseas investment layout: Establish production bases in major markets to avoid trade barriers
Technology Cooperation Introduction: Introducing advanced foreign technology to enhance product competitiveness
Brand Cooperation: Collaborate with internationally renowned brands to enhance brand influence
Standard docking: Actively participate in the formulation of international standards and promote mutual recognition of standards
8. Conclusion and Suggestions
8.1 Main research conclusions
Through in-depth research on the application of Coase's law in plastic product factories, we have drawn the following main conclusions:
The effectiveness of theoretical application
The application of Coase's Law in plastic product factories has significant theoretical basis and practical value. Research has shown that by clearly defining property rights and optimizing transaction costs, enterprises can effectively improve their resource allocation efficiency. A certain plastic factory has achieved a 13.3% reduction in total costs, an increase in overall equipment efficiency (OEE) from 65% to 82%, and an increase in capacity utilization from 75% to 85% by applying Coase's Law. These data fully demonstrate the effectiveness of Coase's law in manufacturing applications.
Diversity of application paths
There are multiple effective paths for plastic product factories to apply Coase's law:
177. Internal production management optimization: Through measures such as equipment property rights division, cost responsibility linkage, and cross departmental coordination mechanisms, production efficiency can be improved by 20-30% and costs can be reduced by 8-15%.
178. Deepening supply chain cooperation: Through long-term supply and demand agreements, capacity sharing, and supplier relationship property rights, supply chain costs can be reduced by 10-20%, and supply stability can be improved by 80%.
179. Development of circular economy: By outsourcing waste disposal rights, constructing shared recycling centers, and innovating circular economy models, it is possible to achieve a waste utilization rate of over 95% and annual cost savings of 15-25%.
The significance of efficiency improvement
Applying Coase's Law can bring multidimensional benefits:
180. Direct economic benefits: The annual net income of a certain plastic factory increased by 14.7 million yuan, with an investment payback period of only 2.5 years. According to the industry average, applying Coase's Law can increase a company's profit margin by 3-5 percentage points.
181. Improved operational efficiency: production cycle shortened by 30-50%, on-time delivery rate increased to 98%, and inventory turnover rate increased by over 50%.
182. Enhanced competitiveness: The comprehensive competitiveness score has increased by 43.5%, the market share has grown by 20%, and customer satisfaction has increased to over 95%.
The Importance of Risk Prevention and Control
In the process of applying Coase's Law, there are various risks that need to be addressed, and a comprehensive prevention and control system needs to be established
183. Property rights definition risk: may lead to disputes between departments, and it is necessary to establish standardized property rights definition procedures and dispute resolution mechanisms.
184. Long term agreement risks: Faced with risks such as price fluctuations and supplier defaults, it is necessary to establish risk sharing mechanisms and emergency plans.
185. Outsourcing quality risk: may affect product quality, requiring the establishment of a strict quality control system.
186. Environmental change risk: Economic situation, policy regulations, and changes in international trade environment may affect application effectiveness, requiring flexible response capabilities.
The necessity of differentiation strategy
Different types of plastic factories need to adopt differentiated application strategies:
187. Classified by scale:
Small businesses (<50 million): focus on internal optimization, with low investment and quick results
Medium sized enterprises (500
)







